GLOSSARY
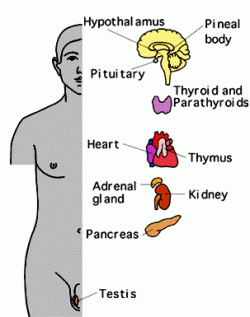
Hypothalmus: The part of the brain that lies below the thalamus, forming the major portion of the ventral region of the diencephalon and functioning to regulate bodily temperature, certain metabolic processes, and other autonomic activities.
Pineal Body: An unpaired, elongated, club-shaped, knoblike or threadlike organ attached by a stalk to the roof of the vertebrate forebrain. Also known as conarium; epiphysis.
Pituitary Gland: A small oval endocrine gland attached to the base of the vertebrate brain and consisting of an anterior and a posterior lobe, the secretions of which control the other endocrine glands and influence growth, metabolism, and maturation. Also called hypophysis, pituitary body.
Thyroid Gland: A two-lobed endocrine gland found in all vertebrates, located in front of and on either side of the trachea in humans, and producing various hormones, such as triiodothyronine and calcitonin.
Parathyroid Gland: Any of usually four small kidney-shaped glands that lie in pairs near or within the posterior surface of the thyroid gland and secrete parathyroid hormone.
Heart: The chambered muscular organ in vertebrates that pumps blood received from the veins into the arteries, thereby maintaining the flow of blood through the entire circulatory system.
Thymus: A single unpaired gland located in the mediastinum that is the primary central gland of the lymphatic system. The T cells of the cell-mediated immune response develop in this gland before migrating to the lymph nodes and spleen.
Adrenal Gland: Either of two small, dissimilarly shaped endocrine glands, one located above each kidney, consisting of the cortex, which secretes several steroid hormones, and the medulla, which secretes epinephrine. Also called suprarenal gland.
Kidney: Either one of a pair of organs in the dorsal region of the vertebrate abdominal cavity, functioning to maintain proper water and electrolyte balance, regulate acid-base concentration, and filter the blood of metabolic wastes, which are then excreted as urine
Pancreas: A long, irregularly shaped gland in vertebrates, lying behind the stomach, that secretes pancreatic juice into the duodenum and insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin into the bloodstream.
Testis: The reproductive gland in a male vertebrate, the source of spermatozoa and the androgens, normally occurring paired in an external scrotum in humans and certain other mammals.
Ovaries: The usually paired female or hermaphroditic reproductive organ that produces ova and, in vertebrates, estrogen and progesterone.
